About Neon Pothos

Neon Pothos Introduction
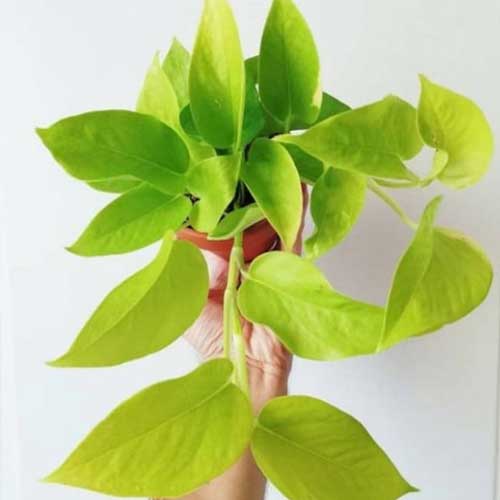
Neon Pothos, scientifically known as Epipremnum aureum ‘Neon’, is a vibrant cultivar of the popular golden pothos or devil’s ivy. This striking houseplant is renowned for its bright, lime-green foliage that seems to glow, especially in low light conditions. Native to the Solomon Islands in the South Pacific, the Neon Pothos has become a beloved houseplant worldwide due to its easy care requirements and eye-catching appearance.
Unlike its variegated cousins, the Neon Pothos features solid-colored leaves that maintain their vivid chartreuse hue throughout the plant’s life, providing it receives good care. The heart-shaped leaves grow on long, trailing vines that can reach impressive lengths when given proper support. In its natural habitat, this plant can climb trees and other structures, but as a houseplant, it is often grown in hanging baskets or trained to climb trellises or moss poles.
The Neon Pothos is prized for its air-purifying qualities, ability to thrive in various light conditions, and its forgiving nature when it comes to care. It’s an excellent choice for both novice and experienced plant enthusiasts, adding a pop of color to any indoor space. While it rarely flowers in indoor settings, its lush foliage more than makes up for the lack of blooms, providing year-round interest and a tropical feel to homes and offices alike.
Neon Pothos Care & Growing Guide
Caring for a Neon Pothos is relatively straightforward, making it an ideal plant for beginners or those with busy lifestyles. This resilient houseplant adapts well to various indoor environments and can tolerate some neglect, though it thrives best with consistent care.
Light is a crucial factor in maintaining the vibrant color of your Neon Pothos. While it can survive in low light conditions, bright, indirect light is ideal for preserving its signature neon hue. Too much direct light can scorch the leaves, so it’s best to place the plant near a north- or east-facing window, or a few feet away from a south- or west-facing window with filtered light. Rotate the plant occasionally to ensure even growth and color distribution.
Watering is another essential aspect of Neon Pothos care. These plants prefer their soil to dry out slightly between waterings. A good rule of thumb is to water when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch or the moisture meter reads 4 and is nearing 3. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so it’s better to err on the side of underwatering. During the active growing season (spring through fall), you may need to water more frequently than in the cooler winter months. Always use well-draining soil and a pot with drainage holes to prevent water from sitting around the roots.
 Soil
Soil
Neon Pothos thrives in well-draining, slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.1 to 6.5. A good potting mix for this plant should be light and airy, allowing for proper drainage while retaining some moisture. A mixture of peat moss, perlite or pumice, and regular potting soil in equal parts works well.
The soil should be rich in organic matter to provide nutrients and retain moisture without becoming waterlogged. Adding a small amount of orchid bark or coconut coir can improve aeration and drainage. Avoid heavy, clay-like soils that can lead to root rot.
Soil problems to watch out for include:
1. Poor drainage: Can lead to root rot and fungal diseases.
2. Compaction: Restricts root growth and oxygen availability.
3. Inappropriate pH: Can affect nutrient uptake.
4. Salt build-up: Often from over-fertilization, can damage roots.
5. Nutrient deficiencies: May occur in poor-quality or depleted soil.
6. Pot boundness: Can occur if the plant outgrows its pot, leading to stunted growth.
To maintain optimal soil conditions, repot your Neon Pothos every 1-2 years with fresh potting mix, and ensure the pot has adequate drainage holes.
 Fertilizer
Fertilizer
Neon Pothos benefits from regular fertilization during the growing season (spring through fall). Use a well-balanced, organic houseplant fertilizer diluted to half strength every 4-6 weeks.
Recommended mixture: 5-5-5 or 10-10-10 NPK ratio, diluted to half the recommended strength.
Signs of over-fertilization:
– Brown or burnt leaf tips
– White crust on soil surface
– Wilting despite adequate watering
– Stunted growth
Signs of under-fertilization:
– Pale or yellowing leaves
– Slow growth
– Smaller than normal leaves
Organic alternatives:
– Compost tea
– Worm castings
– Seaweed extract
Neon Pothos is particularly sensitive to fluoride. If using tap water high in fluoride, consider switching to distilled, reverse osmosis, or rainwater.
Reduce or stop fertilization during late fall and winter when growth slows. Resume in spring when new growth appears.
 Watering
Watering
Neon Pothos prefers to have its soil dry out slightly between waterings. Water thoroughly when the top 1-2 inches of soil feels dry to the touch and the moisture meter reads 4, approaching 3. These plants are more tolerant of underwatering than overwatering.
Water quality: Neon Pothos is not particularly fussy about water quality. Tap water is generally fine, but if your tap water is hard or heavily chlorinated, or contains high amounts of fluoride, consider using filtered or distilled water.
Signs of underwatering:
– Drooping or wilting leaves
– Dry, crispy leaf edges
– Slow growth
Signs of overwatering:
– Yellowing leaves, especially lower ones
– Soft, mushy stems
– Mold on soil surface
– Foul odor from the soil
Watering needs change seasonally. During the growing season (spring and summer), water more frequently. In fall and winter, reduce watering as the plant’s growth slows. Always check the soil moisture before watering rather than sticking to a strict schedule.
 Lighting
Lighting
Neon Pothos prefers bright, indirect light to maintain its vibrant color and promote healthy growth. While it can tolerate low light conditions, the plant may lose some of its characteristic neon hue and become more green in color. Avoid placing it in direct light, as this can scorch the leaves.
Signs of insufficient light include:
– Slower growth
– Smaller leaves
– Loss of variegation or neon color
– Leggy or stretched-out growth
Signs of excessive light include:
– Yellowing or bleached leaves
– Crispy, brown edges on leaves
– Wilting or drooping
If natural light conditions are suboptimal, consider using artificial grow lights to supplement. Full-spectrum LED grow lights or fluorescent bulbs placed 6-12 inches above the plant for 12-14 hours a day can help maintain the plant’s vibrant color and promote healthy growth.
 Temperature
Temperature
Neon Pothos thrives in temperatures between 60°F to 80°F (15°C to 27°C). It can tolerate brief periods outside this range but prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures can cause stress and damage.
The plant is somewhat tolerant of temperature fluctuations but prefers consistency. Avoid placing it near drafty windows, air conditioning vents, or heating sources that can cause sudden temperature changes.
Neon Pothos is not frost-hardy and can suffer damage at temperatures below 50°F (10°C). Signs of cold damage include blackened or mushy leaves and stems.
High temperatures above 90°F (32°C) can cause wilting, leaf burn, and increased water loss.
To protect from extreme temperatures:
1. Move the plant away from windows during very hot or cold weather
2. Use insulating curtains or blinds to moderate temperature
3. Avoid placing near heating or cooling vents
4. If outdoors for the summer, bring the plant inside when temperatures drop below 60°F (15°C)
 Humidity
Humidity
Neon Pothos prefers moderate to high humidity levels, ideally between 50%-70%. While it can tolerate average household humidity, higher levels will promote lusher growth and more vibrant foliage.
To increase humidity:
1. Use a pebble tray filled with water placed beneath the pot
2. Group plants together to create a microclimate
3. Use a room humidifier
4. Mist the leaves regularly, especially in dry environments
To decrease humidity (rarely necessary):
1. Improve air circulation with fans
2. Reduce misting and other humidity-increasing measures
Symptoms of low humidity:
– Brown, crispy leaf edges
– Curling leaves
– Slower growth
Symptoms of excessive humidity (rare):
– Fungal growth on leaves or soil
– Soft, mushy stems
Misting is moderately effective for short-term humidity increase. Pebble trays, grouping plants, and humidifiers are more reliable for maintaining consistent humidity levels.
 Propagation
Propagation
Neon Pothos is easily propagated through stem cuttings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a healthy stem with at least 2-3 leaves and 1-2 nodes (the point where leaves emerge from the stem).
2. Cut the stem just below a node using clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears.
3. Remove the lower leaves, leaving 1-2 at the top of the cutting.
4. (Optional) Dip the cut end in rooting hormone to encourage faster root development.
5. Place the cutting in a clear glass of water, ensuring the node is submerged but leaves are above water.
6. Position the glass in a bright, indirect light location.
7. Change the water every 5-7 days to keep it fresh.
8. After 2-3 weeks, roots should begin to develop.
9. Once roots are 1-2 inches long (usually after 4-6 weeks), transplant the cutting into a pot with well-draining soil.
10. Keep the soil consistently moist for the first few weeks as the plant establishes.
Water propagation is the most common and successful method for Neon Pothos, with a success rate of about 90%. Soil propagation is also possible but slightly less reliable. However, if you propagate in soil, you avoid transplant shock, which can occur when moving the plant from water to soil.
The best time to propagate is during the growing season (spring and summer) when the plant is actively growing. New plants typically establish within 1-2 months after being potted.
 Potting
Potting
Neon Pothos prefers pots with good drainage holes to prevent water accumulation. Plastic or ceramic pots work well, but ensure they have drainage holes.
Repotting frequency:
– Young plants: Every 12-18 months
– Mature plants: Every 2-3 years or when pot-bound
Ideal soil composition:
– 1 part peat moss or coconut coir
– 1 part perlite or pumice
– 1 part regular potting soil
Signs that indicate repotting is needed:
– Roots growing out of drainage holes
– Water runs straight through the pot when watering
– Plant seems top-heavy or unstable
– Slowed growth despite proper care
Repotting process:
1. Water the plant a day before repotting to reduce stress.
2. Gently remove the plant from its current pot.
3. Loosen the root ball and trim any rotted or excessively long roots.
4. Place fresh potting mix in the new pot (no more than 1-2 inches larger in diameter).
5. Position the plant in the new pot at the same depth it was previously growing.
6. Fill around the roots with fresh potting mix, gently tamping down to remove air pockets.
7. Water thoroughly and place in a bright, indirect light location.
8. Avoid fertilizing for 4-6 weeks to allow the plant to adjust to its new pot. Feed the plant after new growth appears.
 Pruning
Pruning
Pruning Neon Pothos: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best Time for Pruning
Spring and summer (active growing seasons)
Frequency
As needed, typically 2-3 times per year
Purpose
- Control size and shape
- Promote bushier growth
- Remove damaged or yellowing leaves
- Propagate new plants
Tools Needed
- Clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears
- Rubbing alcohol for sterilization
Step-by-Step Guide
- Sterilize your pruning tools with rubbing alcohol.
- Identify the areas you want to prune, focusing on long, leggy vines or damaged leaves.
- Cut just above a leaf node (where a leaf meets the stem) at a 45-degree angle.
- For size control, cut back longer vines to your desired length.
- To promote bushier growth, pinch off the growing tips of stems.
- Remove any yellowing or damaged leaves by cutting at the base of the leaf stem.
- Dispose of pruned material or use healthy cuttings for propagation.
Aftercare
Water the plant lightly after pruning and place it in a location with bright, indirect light. Avoid fertilizing for 2-3 weeks post-pruning.
Special Considerations
Neon Pothos is a fast grower, so regular pruning helps maintain its shape and promotes fuller growth. Don’t be afraid to prune fairly aggressively—the plant will recover quickly.
 Blooming
Blooming
Neon Pothos rarely blooms indoors. In its natural habitat, it may produce small, inconspicuous flowers on a spadix surrounded by a spathe, typical of the Araceae family. However, the plant is primarily grown for its foliage rather than its flowers. When it does bloom, it’s usually in mature plants during the spring or summer months under optimal conditions of high humidity and bright, indirect light.
 Pests and Diseases
Pests and Diseases
Pests
Common issues
Spider mites
Mealybugs
Scale insects
Symptoms
Spider mites: Fine webbing on leaves, tiny moving dots, yellowing leaves
Mealybugs: White, cottony masses on stems and leaf joints, yellow splotches on leaves
Scale: Small, brown, shell-like bumps on stems and leaves, yellowing on leaves
Treatment
Isolate infected plants
Wipe leaves with a damp cloth to remove pests
Spray with neem oil, insecticidal soap, and/or 91% or 70% isopropyl alcohol
For severe infestations, use systemic insecticides
Diseases
Common issues
Root rot
Leaf spot
Bacterial blight
Symptoms
Root rot: Yellowing leaves, mushy stems, foul odor from soil
Leaf spot: Brown or black spots on leaves
Bacterial blight: Water-soaked lesions on leaves, rapidly spreading
Treatment
Root rot: Remove affected parts, repot in fresh, well-draining soil
Leaf spot: Remove affected leaves, improve air circulation, avoid wetting leaves when watering
Bacterial blight: Remove infected parts, sterilize tools, use copper-based fungicides
 Special Features
Special Features
Neon Pothos is renowned for its vibrant, chartreuse foliage that seems to glow, especially in low light conditions. This unique coloration makes it a standout among houseplants, adding a pop of color to any indoor space. The plant is also known for its air-purifying qualities, effectively removing indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, xylene, and benzene. Its trailing vines can be trained to climb trellises or allowed to cascade from hanging baskets, making it a versatile choice for various decorative applications. Additionally, its low-maintenance nature and adaptability to different light conditions make it an excellent choice for both novice and experienced plant enthusiasts.
 Plant Benefits
Plant Benefits
Neon Pothos is primarily valued for its ornamental qualities and air-purifying abilities rather than herbal or pharmaceutical benefits. However, it has been noted to have some potential health benefits when used in indoor spaces:
1. Air Purification: Neon Pothos is effective at removing indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, xylene, and benzene, which can contribute to improved air quality and potentially better respiratory health.
2. Stress Reduction: Like many houseplants, the presence of Neon Pothos in living or working spaces may contribute to reduced stress levels and improved mood.
3. Increased Humidity: The plant naturally releases water vapor through transpiration, which can slightly increase humidity levels in a room, potentially benefiting respiratory comfort.
4. Productivity Boost: Studies have shown that the presence of plants in work environments can increase productivity and creativity.
It’s important to note that while these benefits are generally associated with houseplants, Neon Pothos should not be consumed or used for medicinal purposes, as it is toxic if ingested.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
Neon Pothos is a patented variety of Epipremnum aureum, developed for its unique, bright coloration. Unlike other pothos varieties, it doesn’t have variegation, maintaining its solid neon-green color throughout its life. In its natural habitat, it can grow to enormous sizes, but as a houseplant, it’s easily managed with regular pruning. While it’s commonly grown as a trailing plant, it can be trained to climb, mimicking its natural growth pattern in tropical forests.
 Life Cycle
Life Cycle
Neon Pothos is a perennial vine that can live for many years with proper care. In its natural habitat, it goes through distinct growth stages:
1. Seedling stage: Rarely seen in cultivation, as pothos is usually propagated by cuttings.
2. Juvenile stage: This is the form most commonly seen in houseplants, with heart-shaped leaves and thin stems.
3. Adult stage: In nature, as the plant climbs trees, it develops larger, split leaves. This stage is rarely reached indoors.
As a houseplant, Neon Pothos remains in its juvenile form indefinitely. It has a continuous growth cycle, actively growing during spring and summer and slowing down in fall and winter. The plant doesn’t have a true dormancy period but growth significantly slows in cooler months.
Neon Pothos can potentially live for decades with proper care, continually producing new growth and shedding older leaves. Regular pruning helps maintain its shape and encourages bushier growth.
 Are Neon Pothos Poisonous, Toxic
Are Neon Pothos Poisonous, Toxic
Neon Pothos is toxic to cats, dogs, and humans if ingested. All parts of the plant contain calcium oxalate crystals, which can cause irritation and swelling of the mouth, tongue, and throat if chewed or eaten. In pets, symptoms may include drooling, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and oral pain. In severe cases, it can cause breathing difficulties due to swelling of the airways. For humans, especially children, ingestion can lead to similar symptoms, including burning and swelling of the lips, mouth, and tongue, as well as potential stomach upset. While rarely fatal, it can cause significant discomfort. If ingestion occurs, rinse the mouth thoroughly and seek medical attention or veterinary care. To prevent incidents, keep the plant out of reach of children and pets, and consider alternative non-toxic plants if you have curious pets or young children.
 Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I water my Neon Pothos?
Water your Neon Pothos when the top 1-2 inches of soil feel dry to the touch, and the moisture meter reads 4, approaching 3. This usually means watering once every 1-2 weeks, depending on light and humidity conditions.
Is Neon Pothos toxic to pets?
Yes, Neon Pothos is toxic to cats and dogs if ingested. It contains calcium oxalate crystals which can cause irritation and swelling of the mouth and digestive tract.
How much light does a Neon Pothos need?
Neon Pothos prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid direct light, as it can scorch the leaves.
How do I propagate my Neon Pothos?
Neon Pothos can be easily propagated through stem cuttings. Cut a stem with 2-3 leaves just below a node, remove the lower leaves, and place the cutting in water until roots develop. They can also be propagated in soil.
Why are my Neon Pothos leaves turning yellow?
Yellowing leaves can be caused by overwatering, underwatering, low light, or nutrient deficiencies. Check the soil moisture and adjust watering accordingly, and ensure the plant is getting enough light and fertilizer.
How often should I fertilize my Neon Pothos?
Fertilize your Neon Pothos every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer) with a well-balanced, organic houseplant fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Can Neon Pothos grow in water permanently?
Yes, Neon Pothos can grow in water permanently. However, it may not grow as vigorously as in soil and will require regular fertilization with a hydroponic fertilizer, or you can use an organic, liquid houseplant fertilizer diluted to 1/4 strength.
How do I make my Neon Pothos fuller?
To make your Neon Pothos fuller, regularly pinch off the growing tips to encourage branching. You can also propagate more cuttings and plant them in the same pot to create a bushier appearance.
Why is my Neon Pothos losing its bright color?
Loss of bright color in Neon Pothos is often due to insufficient light. Move the plant to a brighter location, but avoid direct light. Nutrient deficiencies can also cause color loss, so ensure you are fertilizing regularly.
How often should I repot my Neon Pothos?
Repot your Neon Pothos every 1-2 years, or when it becomes pot-bound. Choose a pot no more than 1-2 inches larger in diameter and use fresh, well-draining potting soil.
 Can I grow Neon Pothos in my indoor space
Can I grow Neon Pothos in my indoor space
Difficulty
Size
Light
Water
Flowering
Pet Safe
Air Purifier
 Epipremnum aureum 'Neon' botanical details
Epipremnum aureum 'Neon' botanical details
Common Name
Other Common Names
Botanical Name
Native Area
Family Name
Plant Type
Genus
Kingdom
 Photo Gallery
Photo Gallery
- Perky Plant fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3RdLA00
- Seaweed extract: https://amzn.to/3z2CsFh
- Rooting hormone: https://amzn.to/3bIXi0t
- Espoma fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3vPa9bs
- Worm compost: https://amzn.to/3HVL01u
- Full-spectrum Light Bulb-Large: https://amzn.to/3yR6VBu
- Full-spectrum Lighting: https://amzn.to/3qhhaiv
- Light meter: https://amzn.to/4dpmp3s
- Moisture meter: https://amzn.to/3TEUu5N
- Hygrometer: https://amzn.to/3Cf6h2F
- Pruning shears: https://amzn.to/3X6oOcg
- ProMix Potting Soil: https://amzn.to/3iVIrjE
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: healthyhouseplants.storenvy.com
- My Perfect Pumice: Healthy Houseplants Store
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: Healthy Houseplants Store
 Plant Puns and Jokes
Plant Puns and Jokes
Why did the Neon Pothos refuse to climb the trellis? It was afraid of heights – it preferred to stay ‘grounded’ in its pot!




 My Neon Pothos Plant Care Recommendations
My Neon Pothos Plant Care Recommendations Buy Neon Pothos Online
Buy Neon Pothos Online