About Dracaena
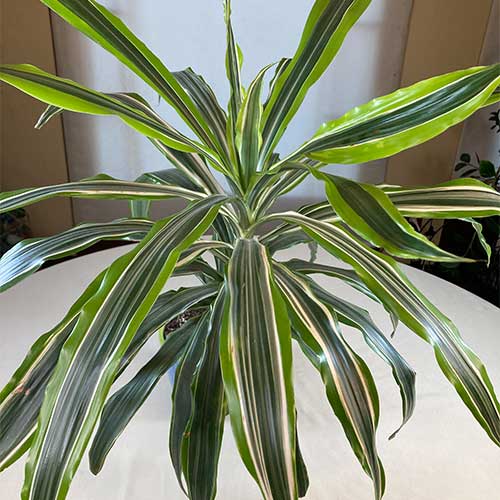

Dracaena Introduction
Dracaena, a diverse genus of plants belonging to the family Asparagaceae, is renowned for its striking foliage and adaptability to indoor environments. Native to Africa, Southern Asia, and Central America, these plants have become popular houseplants worldwide due to their attractive appearance and low maintenance requirements.
Dracaenas are characterized by their long, sword-like leaves that grow in rosettes atop slender stems. The leaves come in a variety of colors and patterns, ranging from solid green to variegated combinations of green, yellow, and red. Some species can grow quite tall, reaching heights of up to 10 feet or more indoors, while others remain compact and bushy.
One of the most notable features of Dracaenas is their air-purifying ability. NASA’s Clean Air Study identified several Dracaena species as effective in removing indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, benzene, and trichloroethylene. This makes them not only aesthetically pleasing but also beneficial for improving indoor air quality in homes and offices.
Dracaena Care & Growing Guide
Caring for Dracaena plants is relatively straightforward, making them an excellent choice for both novice and experienced plant enthusiasts. These resilient plants can thrive in a variety of indoor conditions, but understanding their basic needs will ensure they remain healthy and vibrant.
Light is an important factor in Dracaena care. While they can tolerate low light conditions, they prefer bright, indirect light. Direct sunlight can scorch their leaves, so it’s best to place them near a window with filtered light or a few feet away from a bright window. Rotating the plant regularly will ensure even growth and prevent it from leaning towards the light source.
Watering is another crucial aspect of Dracaena care. These plants prefer to be kept slightly moist but are susceptible to overwatering. Allow the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings, and reduce watering frequency during the winter months when growth slows. It’s important to use water that is free of fluoride and chlorine, as these chemicals can cause leaf tip burn. If using tap water, let it sit out overnight to allow chlorine to evaporate before using it on your Dracaena.
 Soil
Soil
Dracaenas prefer well-draining, slightly acidic soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. A mix of peat moss, perlite, and regular potting soil works well, providing both moisture retention and good drainage. These plants benefit from soil rich in organic matter.
Soil problems to watch for include:
1. Poor drainage: Can lead to root rot. Ensure pots have drainage holes and use a well-draining soil mix.
2. Compaction: Over time, soil can become compacted, reducing aeration. Gently loosen the top layer periodically.
3. Inappropriate pH: If soil is too alkaline, it can cause chlorosis. Use a slightly acidic potting mix or amend with peat moss.
4. Salt build-up: Excess fertilizer can cause salt accumulation. Flush the soil thoroughly every few months.
5. Nutrient deficiencies: Yellowing leaves may indicate nutrient deficiencies. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer during the growing season.
6. Root boundness: If roots are circling the bottom of the pot, it’s time to repot into a larger container.
 Fertilizer
Fertilizer
Fertilize Dracaenas monthly during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced, water-soluble houseplant fertilizer diluted to half strength. Reduce or stop fertilization in fall and winter when growth slows.
Signs of over-fertilization include brown leaf tips, leaf burn, or a white crust on the soil surface. Under-fertilization may result in pale leaves, slow growth, or leaf loss.
Organic alternatives include compost tea or diluted fish emulsion. Dracaenas are particularly sensitive to fluoride, so avoid fertilizers containing this element.
Common nutrient deficiencies in Dracaenas include:
1. Iron: Causes yellowing between leaf veins
2. Magnesium: Results in yellowing of older leaves
3. Nitrogen: Leads to overall yellowing and stunted growth
Address these issues with appropriate, balanced fertilizers or specific nutrient supplements as needed.
 Watering
Watering
Dracaenas prefer to be kept slightly moist but are drought-tolerant. Water when the top inch of soil feels dry. These plants are sensitive to fluoride and chlorine, so use distilled water, rainwater, or let tap water sit out overnight before using.
Signs of underwatering include drooping leaves and dry, crispy leaf edges. Overwatering symptoms include yellowing leaves, soft, mushy stems, and a rotting smell from the soil.
Watering needs change seasonally:
– Spring/Summer (growing season): Water more frequently, keeping soil lightly moist.
– Fall/Winter: Reduce watering as growth slows, allowing soil to dry out more between waterings.
Always check soil moisture before watering and adjust based on the plant’s specific needs and environmental conditions.
 Lighting
Lighting
Dracaenas thrive in bright, indirect light but can tolerate lower light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight as it can scorch the leaves. Place them near east or north-facing windows for optimal light exposure. If natural light is limited, they can adapt to fluorescent lighting.
Signs of insufficient light include slow growth, small new leaves, and loss of variegation in colored varieties. Excessive light can cause leaf burn, visible as brown spots or edges on the leaves.
To adjust lighting:
1. Use sheer curtains to filter strong sunlight.
2. Move the plant closer to or further from windows as needed.
3. Supplement with grow lights if natural light is inadequate.
 Temperature
Temperature
Dracaenas thrive in temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). They can tolerate brief periods outside this range but prefer consistency. Avoid placing them near drafty windows or air conditioning/heating vents.
These plants are sensitive to cold and can suffer damage below 50°F (10°C). Protect them from sudden temperature drops and cold drafts. In summer, they can tolerate slightly higher temperatures but should be shielded from intense heat.
If exposed to temperatures outside their comfort zone, Dracaenas may show stress through leaf drop or discoloration. To protect them, move plants away from windows during extreme weather and use insulating materials if necessary during cold spells.
 Humidity
Humidity
Dracaenas prefer moderate humidity levels, ideally between 40-50%. They can tolerate average indoor humidity but will thrive with slightly higher levels. Low humidity can cause brown leaf tips and edges, while excessively high humidity may lead to fungal issues.
To increase humidity:
1. Use a pebble tray filled with water placed beneath the pot.
2. Group plants together to create a microclimate.
3. Use a room humidifier.
4. Mist the leaves occasionally, but avoid this if it leads to water sitting on leaves for extended periods.
To decrease humidity, improve air circulation around the plant and avoid overwatering. Regular monitoring and adjusting based on the plant’s response will help maintain optimal humidity levels.
 Propagation
Propagation
Dracaenas can be propagated through stem cuttings or air layering. Here’s a step-by-step guide for stem cutting propagation:
1. Choose a healthy stem with at least two leaf nodes.
2. Cut the stem at a 45-degree angle, about 4-6 inches long.
3. Remove lower leaves, leaving 2-3 at the top.
4. (Optional) Dip the cut end in rooting hormone.
5. Plant the cutting in a well-draining potting mix.
6. Water lightly and place in bright, indirect light.
7. Maintain high humidity by covering with a clear plastic bag.
8. Keep soil slightly moist but not waterlogged.
9. Roots should develop in 3-4 weeks.
10. Once new growth appears, remove the plastic and care for as a mature plant.
Air layering is more successful for larger plants but takes longer. Stem cuttings are easier and quicker for most home gardeners.
The best time to propagate is during the growing season (spring to early summer). New plants typically establish in 1-2 months, depending on conditions.
 Potting
Potting
Dracaenas prefer pots with good drainage holes. Choose a container 1-2 inches larger in diameter than the current pot when repotting. Use a well-draining potting mix as described in the soil section.
Repot every 2-3 years or when roots begin to grow through drainage holes. Signs that repotting is needed include:
1. Roots circling the bottom of the pot
2. Water running straight through the pot without being absorbed
3. Slowed growth or nutrient deficiencies
4. Plant becoming top-heavy or unstable
When repotting:
1. Gently remove the plant from its current pot
2. Loosen the root ball and trim any damaged roots
3. Place in the new pot with fresh soil
4. Water thoroughly and place in a shaded area for a few days to recover
Avoid overpotting, as this can lead to waterlogged soil and root rot. For larger specimens, consider root pruning to maintain size without increasing pot size.
 Pruning
Pruning
Best Time for Pruning
Prune Dracaenas during the active growing season, typically spring or early summer.
Frequency
Prune as needed to maintain shape and size, usually once or twice a year.
Purpose
Pruning helps control size, remove dead or yellowing leaves, and encourage bushier growth.
Tools Needed
- Clean, sharp pruning shears or scissors
- Rubbing alcohol for sterilization
Step-by-Step Guide
- Sterilize pruning tools with rubbing alcohol.
- Identify dead, yellowing, or damaged leaves for removal.
- Cut off these leaves at the base where they meet the stem.
- To control height, cut the main stem at the desired point, just above a leaf node.
- For bushier growth, prune the tips of stems to encourage branching.
- Remove any crossing or rubbing branches to improve air circulation.
Aftercare
After pruning, water the plant lightly and place it in a location with bright, indirect light. Avoid fertilizing for a few weeks to allow the plant to recover.
Special Considerations
Dracaenas can be sensitive to pruning. Never remove more than 1/3 of the plant at once. The cut stem may ooze sap; this is normal and will stop on its own.
 Blooming
Blooming
Dracaenas rarely bloom indoors. In their natural habitat, they may produce small, fragrant flowers in spring or summer. The blooming period is usually short-lived, lasting a few weeks. Optimal conditions for blooming include bright, indirect light, consistent temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C), and proper fertilization. Flowers are typically white or pale in color and grow in clusters.
 Pests and Diseases
Pests and Diseases
Pests
Common issues
Spider mites
Mealybugs
Scale insects
Symptoms
Spider mites: Fine webbing on leaves, stippling on leaf surfaces
Mealybugs: White, cottony masses on leaves and stems
Scale: Small, brown, shell-like bumps on stems and leaves
Treatment
Isolate affected plants
Wipe leaves with a damp cloth to remove pests
Apply insecticidal soap or neem oil
For severe infestations, use systemic insecticides
Diseases
Common issues
Root rot
Leaf spot
Symptoms
Root rot: Yellowing leaves, wilting, soft and brown roots
Leaf spot: Brown or black spots on leaves
Treatment
Root rot: Remove affected roots, repot in fresh, well-draining soil, reduce watering
Leaf spot: Remove affected leaves, improve air circulation, avoid overhead watering
 Special Features
Special Features
Dracaenas are known for their air-purifying qualities, effectively removing indoor air pollutants like formaldehyde and benzene. Many species have striking variegated leaves, adding visual interest to indoor spaces. Some varieties, such as Dracaena fragrans, can produce fragrant flowers, though this is rare in indoor conditions.
 Plant Benefits
Plant Benefits
Dracaena plants are known for their air-purifying properties, effectively removing indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, benzene, and trichloroethylene. While not typically used for herbal or pharmaceutical purposes, their ability to improve indoor air quality can contribute to better overall health and well-being in living spaces.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
Dracaenas are often used in feng shui practices to promote positive energy in homes and offices. Some species, like Dracaena cinnabari (the Dragon Blood Tree), produce a red resin that has been used traditionally in various cultures for its supposed medicinal properties.
 Life Cycle
Life Cycle
Dracaenas are perennial plants with a relatively slow growth rate. In their natural habitat, they can live for many years, with some species potentially living for decades. As houseplants, their lifespan can vary based on care but typically ranges from 10-15 years or more. They go through a cycle of active growth during spring and summer, followed by a period of dormancy in fall and winter. Proper care throughout these cycles, including adjusting watering and fertilization, is crucial for their long-term health and vitality.
 Are Dracaena Poisonous, Toxic
Are Dracaena Poisonous, Toxic
Dracaena plants are toxic to cats and dogs if ingested. The toxic compounds are saponins, which can cause vomiting (with or without blood), depression, lack of appetite, excessive salivation, and dilated pupils in cats and dogs. The leaves and stems are the most toxic parts. While not usually fatal, ingestion can lead to significant discomfort and potentially serious symptoms. If ingestion is suspected, contact a veterinarian immediately. To prevent toxicity, keep plants out of reach of pets and consider alternative pet-safe plants if you have curious animals.
 Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I water my Dracaena plant?
Water your Dracaena when the top inch of soil feels dry. This is typically every 7-10 days, but can vary based on environmental conditions.
Is Dracaena toxic to pets?
Yes, Dracaena plants are toxic to cats and dogs if ingested. Keep them out of reach of pets.
How much light does a Dracaena need?
Dracaenas prefer bright, indirect light but can tolerate lower light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight as it can scorch the leaves.
How do I propagate a Dracaena plant?
Dracaenas can be propagated through stem cuttings or air layering. Stem cuttings can be rooted in water or soil.
Why are the leaves on my Dracaena turning yellow?
Yellowing leaves can be caused by overwatering, underwatering, low humidity, or nutrient deficiencies. Check the soil moisture and adjust care accordingly.
How often should I fertilize my Dracaena?
Fertilize monthly during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced, water-soluble houseplant fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Can Dracaenas grow in low light?
While Dracaenas prefer bright, indirect light, they can tolerate low light conditions. However, growth may be slower and variegated varieties may lose some color.
How big do Dracaena plants get?
Dracaena size varies by species, but indoor plants can range from small tabletop varieties to large floor specimens reaching up to 10 feet tall.
How do I prune my Dracaena plant?
Prune Dracaenas during the growing season by cutting the main stem at the desired height. New growth will sprout below the cut. Remove dead or yellowing leaves as needed.
Are Dracaenas good air purifiers?
Yes, Dracaenas are known for their air-purifying qualities. They can help remove indoor air pollutants such as formaldehyde, benzene, and trichloroethylene.
 Can I grow Dracaena in my indoor space
Can I grow Dracaena in my indoor space
Difficulty
Size
Light
Water
Flowering
Pet Safe
Air Purifier
 Dracaena spp. botanical details
Dracaena spp. botanical details
Common Name
Other Common Names
Botanical Name
Native Area
Family Name
Plant Type
Genus
Kingdom
 Photo Gallery
Photo Gallery
- Perky Plant fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3RdLA00
- Seaweed extract: https://amzn.to/3z2CsFh
- Rooting hormone: https://amzn.to/3bIXi0t
- Espoma fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3vPa9bs
- Worm compost: https://amzn.to/3HVL01u
- Full-spectrum Light Bulb-Large: https://amzn.to/3yR6VBu
- Full-spectrum Lighting: https://amzn.to/3qhhaiv
- Light meter: https://amzn.to/4dpmp3s
- Moisture meter: https://amzn.to/3TEUu5N
- Hygrometer: https://amzn.to/3Cf6h2F
- Pruning shears: https://amzn.to/3X6oOcg
- ProMix Potting Soil: https://amzn.to/3iVIrjE
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: healthyhouseplants.storenvy.com
- My Perfect Pumice: Healthy Houseplants Store
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: Healthy Houseplants Store
As an Amazon Associate, I earn commission from qualifying purchases.
 Plant Puns and Jokes
Plant Puns and Jokes
Why did the Dracaena plant refuse to go on a date? It was too busy dragon its feet!





 My Dracaena Plant Care Recommendations
My Dracaena Plant Care Recommendations Buy Dracaena Online
Buy Dracaena Online