About String of Hearts
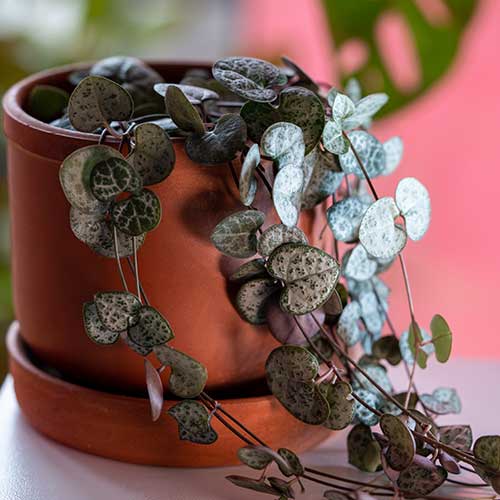

String of Hearts Introduction
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is a captivating trailing succulent native to South Africa, Swaziland, and Zimbabwe. This delicate and charming plant is known for its long, slender vines adorned with small, heart-shaped leaves. The leaves are typically green with silver marbling on the upper surface and purple undersides, creating a stunning visual effect.
One of the most notable features of the String of Hearts is its unique growth habit. As a trailing plant, it can grow up to 3-4 feet long, making it perfect for hanging baskets or as a cascading accent in mixed containers. The plant’s vines are thin and wiry, allowing them to gracefully drape over the edges of pots or climb up trellises with minimal support.
In addition to its attractive foliage, the String of Hearts produces small, tubular flowers that resemble miniature lanterns. These flowers are typically pink or purple and appear sporadically throughout the growing season. While not as showy as the foliage, the flowers add an extra layer of interest to this already fascinating plant. The String of Hearts is also known for its ability to produce small tubers along its stems, which can be used for propagation.
String of Hearts Care & Growing Guide
Caring for a String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is relatively straightforward, making it an excellent choice for both novice and experienced plant enthusiasts. This succulent vine thrives in bright, indirect light and prefers to dry out slightly between waterings, mimicking its natural habitat in South Africa.
When it comes to watering, it’s essential to strike a balance. Allow the top inch or two of soil to dry out completely before watering thoroughly. During the growing season (spring and summer), you may need to water more frequently, while in winter, reduce watering to prevent overwatering and root rot. The String of Hearts is drought-tolerant and can withstand periods of neglect, but consistent care will result in healthier, more vigorous growth.
Fertilization should be done sparingly, as the String of Hearts doesn’t require heavy feeding. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength once a month during the growing season. In terms of soil, a well-draining succulent or cactus mix is ideal. This plant appreciates good air circulation around its roots, so choose a pot with drainage holes and consider adding perlite or coarse sand to improve drainage. Regular pruning can help maintain the plant’s shape and encourage bushier growth, while propagation through stem cuttings or tubers is an easy way to expand your collection.
 Soil
Soil
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) thrives in well-draining soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0-7.0. The ideal soil composition should be a mix of regular potting soil, coarse sand, and perlite or pumice to ensure excellent drainage. A commercial cactus or succulent mix can also work well.
The soil should be light and airy to prevent water retention and root rot. Adding organic matter like coco coir or peat moss can help retain some moisture while still allowing for proper drainage. The ideal soil acidity range is slightly acidic to neutral, but the plant can tolerate a wider range if other conditions are optimal.
Specific soil amendments that benefit the String of Hearts include:
– Coarse sand or perlite for improved drainage
– Vermiculite to help retain some moisture
– A small amount of compost or worm castings for nutrients
Proper soil composition directly affects the plant’s health and growth. Well-draining soil prevents root rot and fungal diseases, while the right pH and nutrient balance promote healthy growth and vibrant foliage.
Soil problems to watch out for include:
– Poor drainage: Can lead to root rot and fungal issues
– Compaction: Restricts root growth and oxygen availability
– Inappropriate pH: Can affect nutrient uptake
– Salt build-up: Can occur from hard water or over-fertilization
– Nutrient deficiencies: May result in yellowing leaves or stunted growth
– Root boundness: Can occur if the plant outgrows its pot, restricting growth and nutrient uptake
 Fertilizer
Fertilizer
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) has relatively low fertilizer needs. During the growing season (spring and summer), feed the plant with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength once a month.
Recommended mixture:
– Use a balanced 10-10-10 or 20-20-20 NPK fertilizer
– Dilute to half the recommended strength
– Alternatively, use a fertilizer specifically formulated for succulents
Optimal fertilizing schedule:
– Feed monthly during spring and summer
– Reduce or stop fertilizing in fall and winter when growth slows
Signs of over-fertilization:
– Salt buildup on soil surface
– Leaf burn or browning edges
– Rapid, weak growth
Signs of under-fertilization:
– Slow growth
– Pale or yellowing leaves
– Smaller than normal leaves
Organic fertilizer alternatives:
– Compost tea
– Worm castings
– Diluted seaweed extract
Specific nutrient requirements:
– The String of Hearts doesn’t have high nutrient demands
– A slight nitrogen deficiency can encourage more compact growth and better color
– Phosphorus is important for root development and flowering
Common deficiencies:
– Iron deficiency can cause yellowing leaves with green veins
– Magnesium deficiency may result in yellowing of older leaves
Note: It’s generally better to under-fertilize than over-fertilize this plant. When in doubt, use less fertilizer or fertilize less frequently.
 Watering
Watering
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) prefers to dry out slightly between waterings. During the growing season (spring and summer), water thoroughly when the top 1-2 inches of soil feel dry to the touch. In winter, reduce watering frequency to prevent overwatering and root rot.
Water quality preferences:
– Rainwater or distilled water is ideal
– If using tap water, allow it to sit out overnight to allow chlorine to dissipate
Signs of underwatering:
– Shriveled, wrinkled leaves
– Dry, crispy leaf edges
– Slow growth or dormancy
Signs of overwatering:
– Yellowing or translucent leaves
– Soft, mushy stems
– Fungal growth on soil surface
– Root rot
Watering needs change seasonally:
– Spring/Summer: More frequent watering as the plant actively grows
– Fall/Winter: Reduce watering as growth slows
During different growth stages:
– Young plants may require slightly more frequent watering
– Mature plants are more drought-tolerant
– Flowering plants may need a slight increase in water
 Lighting
Lighting
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) thrives in bright, indirect light. It can tolerate some direct morning sun but should be protected from harsh afternoon sunlight. An east or west-facing window is ideal, providing the plant with sufficient light without risking sunburn.
Signs of insufficient light:
– Elongated, spindly growth
– Increased space between leaves
– Smaller, paler leaves
– Slow or stunted growth
Signs of excessive light:
– Bleached or scorched leaves
– Dry, crispy leaf edges
– Leaf drop
To adjust lighting if natural conditions are suboptimal:
1. Use sheer curtains to filter strong direct sunlight
2. Move the plant further from or closer to the light source as needed
3. Supplement with grow lights if natural light is insufficient
4. Rotate the plant regularly to ensure even growth and light exposure
 Temperature
Temperature
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) thrives in average room temperatures between 60-80°F (15-27°C). It can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures down to 50°F (10°C) but should be protected from frost and extreme cold.
Temperature tolerance:
– The plant can handle brief periods of temperatures outside its ideal range but prolonged exposure can stress the plant.
– It’s more tolerant of heat than cold, but excessive heat can lead to increased water loss and stress.
Cold sensitivity:
– Avoid exposing the plant to temperatures below 50°F (10°C).
– Cold drafts from windows or air conditioning units can damage the plant.
Heat sensitivity:
– While tolerant of warm temperatures, extreme heat (above 90°F/32°C) can cause stress.
– High heat combined with direct sunlight can lead to leaf scorching.
Protecting from extreme temperatures:
1. Move the plant away from cold windows in winter.
2. Use insulating curtains or blinds to protect from cold drafts.
3. In summer, move the plant away from hot, sunny windows.
4. Avoid placing near heating vents or air conditioning units.
5. If outdoors, bring the plant inside when temperatures drop below 50°F (10°C) or rise above 90°F (32°C).
Tip: Maintain consistent temperatures as much as possible. Sudden temperature fluctuations can stress the plant.
 Humidity
Humidity
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is generally tolerant of average household humidity levels, typically preferring a range between 40-50%. However, it can adapt to both higher and lower humidity environments.
To increase humidity:
1. Use a pebble tray filled with water placed beneath the plant
2. Group plants together to create a microclimate
3. Use a room humidifier
4. Mist the leaves occasionally, but avoid excessive misting as it can lead to fungal issues
To decrease humidity:
1. Improve air circulation with fans
2. Avoid grouping plants too closely
3. Use a dehumidifier if necessary
Symptoms of low humidity stress:
– Dry, crispy leaf edges
– Slower growth
– Increased susceptibility to pests
Symptoms of high humidity stress:
– Fungal growth on leaves or soil
– Soft, mushy stems
– Increased risk of root rot
Specific humidifying methods:
1. Pebble trays: Effective and low-maintenance, but limited range
2. Misting: Can provide temporary relief but needs frequent repetition
3. Humidifiers: Most effective for maintaining consistent humidity levels
4. Grouping plants: Natural and effective, but may require rearranging your space
 Propagation
Propagation
Propagating the String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is relatively easy and can be done through several methods. Here’s a detailed guide:
1. Stem Cutting Propagation:
Step 1: Choose a healthy stem with several leaves.
Step 2: Cut a 4-6 inch section just below a leaf node.
Step 3: Remove leaves from the bottom 2 inches of the cutting.
Step 4: Allow the cut end to callus for 24 hours.
Step 5: Plant the cutting in well-draining soil or place in water.
Step 6: Keep the soil slightly moist or change water weekly if water propagating.
Step 7: Roots should develop in 2-4 weeks.
2. Layering Propagation:
Step 1: Choose a long, healthy vine.
Step 2: Pin a section of the vine to the soil surface in another pot.
Step 3: Ensure a leaf node is in contact with the soil.
Step 4: Keep the soil lightly moist.
Step 5: Roots will form at the contact point in 2-4 weeks.
Step 6: Once rooted, cut the new plant from the mother plant.
3. Tuber Propagation:
Step 1: Locate aerial tubers on the vines.
Step 2: Gently remove the tuber from the vine.
Step 3: Place the tuber on moist, well-draining soil.
Step 4: Cover lightly with soil, leaving the top exposed.
Step 5: Keep the soil lightly moist.
Step 6: New growth should appear in 2-4 weeks.
Success rates:
– Stem cutting: High success rate, especially in water
– Layering: Very high success rate, but slower
– Tuber propagation: Moderate to high success rate
Best time to propagate:
– Spring and early summer are ideal for propagation
– Avoid propagating during the plant’s dormant winter period
Establishment time:
– Stem cuttings: 4-6 weeks for root development, 2-3 months for significant growth
– Layering: 4-6 weeks for rooting, 1-2 months after separation for establishment
– Tubers: 4-6 weeks for new growth, 2-3 months for a well-established plant
Note: Maintain warm temperatures (70-80°F/21-27°C) and bright, indirect light during propagation for best results.
 Potting
Potting
Potting and repotting requirements for the String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii):
Pot type:
– Use a pot with drainage holes to prevent water accumulation
– Terracotta or clay pots are ideal as they allow excess moisture to evaporate
– Hanging baskets or shallow pots work well for showcasing the trailing vines
Drainage needs:
– Excellent drainage is crucial to prevent root rot
– Add a layer of pebbles or broken pottery at the bottom of the pot for extra drainage
Repotting frequency:
– Repot young plants annually
– Mature plants can be repotted every 2-3 years or when rootbound
Ideal soil composition:
– Use a well-draining succulent or cactus mix
– Add perlite or coarse sand to improve drainage
– A mix of 2 parts potting soil, 1 part perlite, and 1 part coarse sand works well
Signs that indicate repotting is needed:
– Roots growing out of drainage holes
– Plant becoming top-heavy or unstable
– Soil drying out very quickly after watering
– Slowed growth or nutrient deficiencies
Root pruning:
– Gently trim away any dead, damaged, or excessively long roots
– Avoid removing more than 1/3 of the root system
Transitioning to a new pot:
1. Water the plant a day before repotting to reduce stress
2. Gently remove the plant from its current pot
3. Shake off excess soil and inspect roots
4. Place in the new pot with fresh soil mix
5. Ensure the plant is at the same depth as in the previous pot
6. Water lightly and place in a bright, indirect light location
7. Avoid fertilizing for a month to allow the plant to adjust
Minimizing stress during repotting:
– Repot during the growing season (spring or early summer)
– Avoid repotting when the plant is flowering
– Handle the plant gently to minimize root disturbance
– Provide extra humidity and stable conditions after repotting
 Pruning
Pruning
Best Time for Pruning
Spring or early summer, during the active growing season
Frequency
As needed, typically 1-2 times per year
Purpose
- Control size and shape
- Promote bushier growth
- Remove dead or damaged vines
- Prevent the plant from becoming too leggy
Tools
- Clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears
- Rubbing alcohol for sterilization
Step-by-Step Pruning Guide
- Sterilize your pruning tools with rubbing alcohol.
- Identify long, leggy vines or areas where you want to encourage branching.
- Cut just above a leaf node, making a clean, angled cut.
- For general shaping, trim vines to your desired length.
- Remove any dead, yellowing, or damaged vines at their base.
- To encourage bushier growth, pinch off the growing tips of vines.
- Collect healthy cuttings for propagation if desired.
Preparation
Water the plant thoroughly a day before pruning to ensure it’s well-hydrated.
Aftercare
- Place the pruned plant in a bright, indirect light location.
- Reduce watering slightly until new growth appears.
- Monitor for any signs of stress or disease.
Special Considerations
- Avoid heavy pruning during the plant’s dormant winter period.
- Don’t remove more than 1/3 of the plant’s total growth at once.
- Be cautious not to damage the delicate vines while pruning.
- Consider using pruned sections for propagation to expand your collection.
 Blooming
Blooming
The String of Hearts typically blooms sporadically throughout the year, with peak flowering occurring in spring and summer. The blooming period can last for several weeks to months, depending on the growing conditions. Optimal conditions for blooming include bright, indirect light, proper watering, and temperatures between 60-80°F (15-27°C). The flowers are small, tubular, and lantern-shaped, usually pink or purple in color, measuring about 1-2 cm in length.
 Pests and Diseases
Pests and Diseases
Pests
Common issues
Mealybugs, White, cottony masses on leaves and stems, Isolate the plant, remove visible pests with a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol, spray with neem oil or insecticidal soap
Spider mites, Fine webbing on leaves, stippling on leaf surfaces, yellowing leaves, Increase humidity, spray leaves with water to dislodge mites, apply neem oil or introduce predatory mites
Aphids, Clusters of small insects on new growth, distorted leaves, sticky residue, Spray with strong water jet to dislodge, apply insecticidal soap or neem oil, introduce ladybugs as natural predators
Diseases
Common issues
Root rot, Wilting despite moist soil, yellowing leaves, soft, brown roots, Remove affected parts, repot in fresh, well-draining soil, reduce watering frequency
Leaf spot, Brown or black spots on leaves, yellowing around spots, Remove affected leaves, improve air circulation, avoid overhead watering, apply fungicide if severe
Powdery mildew, White, powdery coating on leaves, Improve air circulation, reduce humidity, apply neem oil or fungicide
 Special Features
Special Features
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is known for its unique heart-shaped leaves and delicate trailing vines, making it a popular choice for hanging baskets. It produces small, tubular flowers that resemble tiny lanterns, adding to its charm. The plant also develops small tubers along its stems, which can be used for propagation, giving it an interesting and unusual growth habit.
 Plant Benefits
Plant Benefits
While the String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is not commonly used for herbal or pharmaceutical purposes, it does offer some benefits. As a houseplant, it can help improve indoor air quality by removing small amounts of toxins. The plant’s trailing nature and attractive foliage can also contribute to a more aesthetically pleasing environment, potentially reducing stress and improving mood.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
The String of Hearts is also known for its ability to tolerate periods of drought, making it an excellent choice for forgetful gardeners or those new to plant care. Its unique appearance and low maintenance requirements have made it increasingly popular in interior design and as a gift plant.
 Life Cycle
Life Cycle
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is a perennial succulent vine. It has a relatively slow growth rate but can live for many years with proper care. The plant enters a period of active growth in spring and summer, during which it produces new leaves and elongates its vines. In fall and winter, growth slows down, and the plant may enter a semi-dormant state. Throughout its life cycle, the String of Hearts requires well-draining soil, bright indirect light, and infrequent but thorough watering.
 Are String of Hearts Poisonous, Toxic
Are String of Hearts Poisonous, Toxic
The String of Hearts (Ceropegia woodii) is considered mildly toxic to cats, dogs, and children if ingested. The toxic parts of the plant are primarily the leaves and stems. While severe poisoning is rare, ingestion can cause gastrointestinal upset in pets and humans.
Symptoms of toxicity may include:
– Nausea
– Vomiting
– Diarrhea
– Drooling (in pets)
– Mild stomach discomfort
The severity is generally low to moderate, but it’s still important to prevent ingestion. If ingestion occurs, follow these first aid steps:
1. Remove any remaining plant material from the mouth.
2. Rinse the mouth with water.
3. Offer small sips of water to drink.
4. Monitor for symptoms and contact a healthcare provider or veterinarian if symptoms persist or worsen.
Preventive measures include:
– Keeping the plant out of reach of children and pets
– Educating family members about the plant’s potential toxicity
– Considering alternative, non-toxic plants if you have curious pets or young children
 Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I water my String of Hearts?
Water your String of Hearts when the top 1-2 inches of soil feel dry. This is typically every 1-2 weeks during the growing season and less frequently in winter.
What kind of light does a String of Hearts need?
String of Hearts thrives in bright, indirect light. It can tolerate some direct morning sun but should be protected from harsh afternoon sunlight.
How do I propagate a String of Hearts?
String of Hearts can be propagated through stem cuttings, layering, or by planting the small tubers that form along the vines.
Is String of Hearts toxic to pets?
Yes, String of Hearts is mildly toxic to cats and dogs if ingested. It can cause gastrointestinal upset.
How often should I fertilize my String of Hearts?
Fertilize your String of Hearts monthly during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Why are the leaves on my String of Hearts turning yellow?
Yellowing leaves can be caused by overwatering, poor drainage, or nutrient deficiencies. Ensure your plant has well-draining soil and adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
How do I make my String of Hearts fuller?
To encourage fuller growth, pinch off the growing tips of vines and consider layering some of the vines back into the pot to create new growth points.
What type of soil is best for String of Hearts?
String of Hearts prefers well-draining soil. A mix of regular potting soil, coarse sand, and perlite or a commercial cactus/succulent mix works well.
How often should I repot my String of Hearts?
Young plants can be repotted annually, while mature plants typically need repotting every 2-3 years or when they become rootbound.
Can String of Hearts grow in low light conditions?
While String of Hearts can tolerate lower light conditions, it grows best in bright, indirect light. In low light, growth may be slower and the plant may become leggy.
 Can I grow String of Hearts in my indoor space
Can I grow String of Hearts in my indoor space
Difficulty
Size
Light
Water
Flowering
Pet Safe
Air Purifier
 Ceropegia woodii botanical details
Ceropegia woodii botanical details
Common Name
Other Common Names
Botanical Name
Native Area
Family Name
Plant Type
Genus
Kingdom
 Photo Gallery
Photo Gallery
- Perky Plant fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3RdLA00
- Seaweed extract: https://amzn.to/3z2CsFh
- Rooting hormone: https://amzn.to/3bIXi0t
- Espoma fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3vPa9bs
- Worm compost: https://amzn.to/3HVL01u
- Full-spectrum Light Bulb-Large: https://amzn.to/3yR6VBu
- Full-spectrum Lighting: https://amzn.to/3qhhaiv
- Light meter: https://amzn.to/4dpmp3s
- Moisture meter: https://amzn.to/3TEUu5N
- Hygrometer: https://amzn.to/3Cf6h2F
- Pruning shears: https://amzn.to/3X6oOcg
- ProMix Potting Soil: https://amzn.to/3iVIrjE
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: healthyhouseplants.storenvy.com
- My Perfect Pumice: Healthy Houseplants Store
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: Healthy Houseplants Store
As an Amazon Associate, I earn commission from qualifying purchases.
 Plant Puns and Jokes
Plant Puns and Jokes
Why did the String of Hearts plant go to therapy? It had too many emotional attachments!




 My String of Hearts Plant Care Recommendations
My String of Hearts Plant Care Recommendations Buy String of Hearts Online
Buy String of Hearts Online