About Variegated Wax Plant
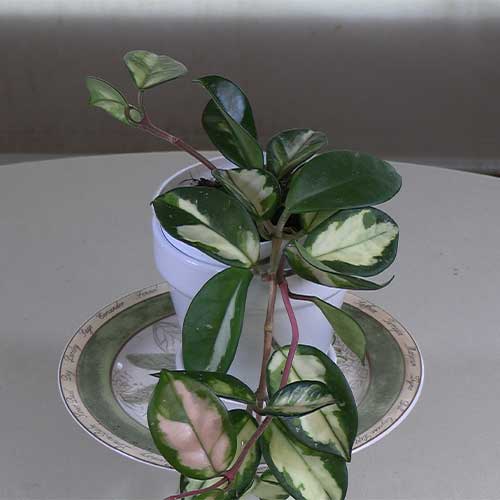

Variegated Wax Plant Introduction
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) is a stunning tropical vine known for its unique foliage and fragrant flowers. Native to Eastern Asia and Australia, this epiphytic plant has become a popular houseplant due to its attractive appearance and relatively low maintenance requirements.
The most striking feature of the Variegated Wax Plant is its thick, waxy leaves that display beautiful cream or yellow variegation against a deep green background. The variegation pattern can vary from plant to plant, making each specimen unique. The leaves are oval-shaped and grow in pairs along trailing vines that can reach several feet in length when properly supported.
In addition to its eye-catching foliage, the Variegated Wax Plant is prized for its clusters of star-shaped flowers. These blooms, which appear in umbels, are typically pink or white with a red center and have a waxy texture that gives the plant its common name. The flowers are known for their sweet, honey-like fragrance that is particularly noticeable in the evening, making it a delightful addition to any indoor space.
Variegated Wax Plant Care & Growing Guide
Caring for a Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) requires attention to its specific needs, but with proper care, it can thrive as a long-lived houseplant. This plant appreciates bright, indirect light, which helps maintain its variegation without risking leaf burn. While it can tolerate lower light conditions, the growth may slow, and the variegation may become less pronounced.
Watering is a crucial aspect of Hoya care. These plants prefer to dry out slightly between waterings, as they are susceptible to root rot if kept too moist. During the growing season (spring and summer), water when the top inch of soil feels dry. In winter, reduce watering frequency to prevent overwatering. Humidity is also important for the Variegated Wax Plant; it thrives in environments with moderate to high humidity, similar to its native tropical habitats.
Fertilization should be done during the growing season with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength. Be cautious not to over-fertilize, as this can lead to salt build-up in the soil and damage the plant. Pruning is generally minimal, mainly to control size or remove any dead or yellowing leaves. When it comes to repotting, Hoyas prefer to be slightly root-bound, so only repot when necessary, typically every 2-3 years or when the plant has outgrown its current container.
 Soil
Soil
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) thrives in well-draining, airy soil that mimics its natural epiphytic growing conditions. The ideal soil composition is a mix of peat moss, perlite, and orchid bark, which provides both moisture retention and excellent drainage. The preferred pH range is slightly acidic to neutral, between 6.1 to 7.5.
For optimal growth, the soil should allow excess water to drain quickly while retaining enough moisture for the roots. A good potting mix for Hoyas might consist of 2 parts peat moss, 1 part perlite, and 1 part orchid bark. This combination ensures proper aeration and prevents water logging, which can lead to root rot.
The soil composition significantly affects the plant’s health and growth. Well-draining soil prevents root rot and fungal diseases, while the slightly acidic pH helps with nutrient uptake. Adding organic matter like compost can improve soil structure and provide slow-release nutrients.
Soil problems to watch for include:
1. Poor drainage: Can lead to root rot and fungal issues.
2. Compaction: Reduces air circulation to roots, impeding growth.
3. Inappropriate pH: Can affect nutrient availability and uptake.
4. Salt build-up: Often from over-fertilization, can damage roots.
5. Nutrient deficiencies: May occur in poor-quality or depleted soil.
6. Root boundness: Can occur if the plant outgrows its pot, restricting growth and nutrient uptake.
To address these issues, ensure proper soil mix, use a pot with drainage holes, flush the soil occasionally to prevent salt build-up, and repot when necessary with fresh, nutrient-rich soil.
 Fertilizer
Fertilizer
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) benefits from regular fertilization during its active growing season, typically spring and summer.
Recommended fertilizer:
– Balanced, water-soluble fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10 or 20-20-20)
– Dilute to half the recommended strength
Fertilization schedule:
– Feed every 2-4 weeks during spring and summer
– Reduce or stop fertilization in fall and winter
Signs of over-fertilization:
1. Brown or crispy leaf edges
2. Salt crust on soil surface
3. Stunted growth
4. Leaf drop
Signs of under-fertilization:
1. Pale or yellowing leaves
2. Slow growth
3. Smaller than normal leaves
4. Poor flowering
Organic fertilizer alternatives:
1. Compost tea
2. Worm castings
3. Fish emulsion (use sparingly due to strong odor)
4. Seaweed extract
Specific nutrient requirements:
– Hoyas generally don’t have high nutrient demands
– Phosphorus can promote blooming
– Calcium and magnesium support overall plant health
Common deficiencies:
1. Iron deficiency: yellowing leaves with green veins
2. Magnesium deficiency: yellowing between leaf veins
3. Nitrogen deficiency: overall yellowing of older leaves
To avoid nutrient issues, use a balanced fertilizer and occasionally flush the soil with plain water to prevent salt build-up. Always follow the less is more approach with fertilizing Hoyas to prevent over-fertilization.
 Watering
Watering
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) prefers a ‘soak and dry’ watering method. Allow the top 1-2 inches of soil to dry out between waterings. During the growing season (spring and summer), this might mean watering once every 7-10 days, while in winter, watering frequency may decrease to once every 2-3 weeks.
Water quality preferences:
– Rainwater or distilled water is ideal
– If using tap water, allow it to sit out overnight to allow chlorine to evaporate
– Avoid using softened water due to its high salt content
Signs of underwatering:
– Wilting or drooping leaves
– Dry, crispy leaf edges
– Slow growth
Signs of overwatering:
– Yellowing leaves
– Soft, mushy stems
– Mold on soil surface
– Root rot (if severe)
Seasonal changes:
– Increase watering frequency during active growth in spring and summer
– Reduce watering in fall and winter when growth slows
Growth stage considerations:
– Young plants may require more frequent watering as they establish
– Mature plants are more drought-tolerant and can withstand longer periods between waterings
Always check the soil moisture before watering and adjust based on the plant’s specific needs and environmental conditions.
 Lighting
Lighting
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) thrives in bright, indirect light. It can tolerate some direct morning sun, but should be protected from harsh afternoon sunlight. The ideal location is near a north or east-facing window where it can receive plenty of light without being exposed to direct sun rays.
Signs of insufficient light:
1. Slow or stunted growth
2. Elongated, leggy stems
3. Loss of variegation
4. Smaller leaves
Signs of excessive light:
1. Yellowing or bleached leaves
2. Crispy, brown leaf edges
3. Leaf drop
4. Sunburn spots on leaves
If natural light conditions are suboptimal, you can adjust by:
1. Using sheer curtains to filter strong direct light
2. Moving the plant closer to or further from the light source
3. Rotating the plant regularly to ensure even light exposure
4. Supplementing with artificial grow lights, especially in low-light environments or during winter months
5. Placing the plant on a pebble tray filled with water to increase humidity, which can help mitigate some effects of strong light
 Temperature
Temperature
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) thrives in temperatures ranging from 60°F to 80°F (15°C to 27°C). It can tolerate slightly higher temperatures but may struggle in cooler conditions.
Ideal temperature range: 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C)
Tips for maintaining optimal temperature:
1. Avoid placing the plant near drafty windows or doors in winter
2. Keep away from air conditioning vents or heaters
3. Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature in the plant’s environment
Temperature fluctuation tolerance:
Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’ can handle minor temperature fluctuations but prefers stable conditions. Sudden changes can stress the plant.
Cold sensitivity:
– Temperatures below 50°F (10°C) can damage the plant
– Signs of cold damage include leaf drop and blackened stems
Heat sensitivity:
– While tolerant of warm temperatures, extreme heat (above 90°F or 32°C) can cause stress
– Signs of heat stress include wilting and leaf scorching
Protecting from extreme temperatures:
1. Move the plant away from windows during very hot or cold weather
2. Use insulating curtains on windows in winter
3. Provide shade or move to a cooler spot during heatwaves
4. Avoid exposing to cold drafts or hot air from heating vents
5. If outdoors, bring the plant inside when temperatures drop below 50°F (10°C)
Maintaining a consistent, comfortable room temperature year-round will help ensure the health and vitality of your Variegated Wax Plant.
 Humidity
Humidity
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) prefers moderate to high humidity levels, ideally between 50-70%. This mimics its natural tropical habitat and promotes healthy growth.
To increase humidity:
1. Use a pebble tray filled with water placed beneath the plant
2. Group plants together to create a microclimate
3. Use a room humidifier
4. Mist the leaves regularly, but avoid wetting the flowers
To decrease humidity (rarely necessary):
1. Improve air circulation with fans
2. Reduce grouping of plants
3. Use a dehumidifier if indoor humidity is excessively high
Symptoms of low humidity stress:
1. Dry, crispy leaf edges
2. Leaf curling
3. Slow growth
4. Flower buds dropping before opening
Symptoms of high humidity stress (uncommon but possible in stagnant air):
1. Fungal growth on leaves or soil
2. Soft, mushy growth
3. Leaf yellowing
Specific humidifying methods:
1. Pebble trays: Effective and low-maintenance, but limited range
2. Misting: Provides temporary boost, requires frequent application
3. Humidifiers: Most effective for maintaining consistent humidity levels
4. Terrariums or humidity domes: Very effective but may limit air circulation
For Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’, a combination of pebble trays and occasional misting often provides adequate humidity without risking overwatering or fungal issues.
 Propagation
Propagation
Propagating the Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) can be done through stem cuttings or leaf cuttings. Stem cuttings are generally more successful and faster to establish.
Step-by-step guide for stem cutting propagation:
1. Choose a healthy stem with at least 2-3 nodes (points where leaves attach).
2. Using clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears, cut a 4-6 inch section just below a node.
3. Remove the lower leaves, leaving 2-3 leaves at the top.
4. (Optional) Dip the cut end in rooting hormone to encourage faster root development.
5. Plant the cutting in a well-draining potting mix (2 parts peat moss, 1 part perlite).
6. Water lightly and place in a warm, bright location with indirect light.
7. Maintain high humidity by covering with a clear plastic bag, leaving it slightly open for air circulation.
8. Keep the soil lightly moist but not waterlogged.
9. Roots should develop in 4-6 weeks. Gently tug on the cutting to check for resistance, indicating root growth.
10. Once roots are established, gradually acclimate the new plant to normal room conditions.
Leaf cutting method (less common, slower):
1. Select a healthy, mature leaf.
2. Cut the leaf off at the base, including the petiole (leaf stem).
3. Insert the petiole into moist, well-draining potting mix.
4. Follow steps 6-10 from the stem cutting method.
Comparison of success rates:
– Stem cuttings: High success rate, faster growth
– Leaf cuttings: Lower success rate, slower growth
Best time to propagate:
– Spring to early summer, when the plant is in active growth
Establishment time:
– Stem cuttings: 4-8 weeks for root development, several months for significant growth
– Leaf cuttings: 2-3 months for root development, up to a year for new growth
Remember that variegated plants may lose some variegation in propagated cuttings, but this often returns as the plant matures.
 Potting
Potting
Potting and repotting requirements for the Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’):
Pot type:
– Use a pot with drainage holes to prevent water logging
– Terracotta or clay pots are ideal as they allow for better air circulation
– Plastic pots are suitable but retain more moisture
Drainage needs:
– Excellent drainage is crucial to prevent root rot
– Add a layer of pebbles or broken pottery at the bottom of the pot for extra drainage
Repotting frequency:
– Every 2-3 years, or when the plant becomes root-bound
– Hoyas prefer to be slightly root-bound, so don’t rush to repot
Ideal soil composition:
– 2 parts peat moss or coco coir
– 1 part perlite or pumice
– 1 part orchid bark
Signs that indicate repotting is needed:
1. Roots growing out of drainage holes
2. Water draining too quickly
3. Plant becoming top-heavy or unstable
4. Slowed growth despite proper care
5. Soil drying out unusually fast
Root pruning:
– Generally not necessary for Hoyas
– If roots are severely bound, gently loosen and trim any damaged or rotting roots
Transitioning to a new pot:
1. Water the plant a day before repotting
2. Gently remove the plant from its current pot
3. Shake off excess soil and inspect roots
4. Place in the new pot with fresh potting mix
5. Ensure the plant is at the same depth as in the previous pot
6. Water thoroughly and place in a bright, indirect light
7. Avoid fertilizing for a month to allow the plant to adjust
Minimizing stress during repotting:
– Repot in spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing
– Avoid repotting when the plant is flowering
– Maintain similar light and temperature conditions after repotting
– Increase humidity slightly to help the plant recover
 Pruning
Pruning
Best Time for Pruning:
Spring or early summer, during the active growing season
Frequency:
As needed, typically once or twice a year
Purpose of Pruning:
- Control size and shape
- Remove dead or yellowing leaves
- Encourage bushier growth
- Remove tangled vines
Tools Needed:
- Clean, sharp pruning shears or scissors
- Rubbing alcohol for sterilizing tools
Step-by-Step Pruning Guide:
- Sterilize your pruning tools with rubbing alcohol.
- Identify dead, yellowing, or damaged leaves and stems.
- Cut these off at the base where they meet the main stem.
- To control size, cut back long vines to the desired length, making cuts just above a leaf node.
- To encourage bushier growth, pinch off the tips of stems.
- Remove any tangled vines to improve air circulation.
- Avoid cutting off healthy spurs (small protrusions) as these are future flowering sites.
Preparation:
Ensure the plant is well-watered a day before pruning to reduce stress.
Aftercare:
- Place the pruned plant in a location with bright, indirect light.
- Avoid fertilizing for 2-4 weeks after pruning.
- Maintain regular watering, but avoid overwatering as the plant adjusts.
Special Considerations:
- Hoyas bloom on old growth, so avoid heavy pruning if you want flowers.
- Save healthy cuttings for propagation if desired.
- Be cautious not to remove too much foliage at once, as this can stress the plant.
 Blooming
Blooming
The Variegated Wax Plant typically blooms in spring and summer, with flowering periods that can last several weeks. Blooms often appear on mature plants when they are at least 2-3 years old. The plant produces clusters of small, star-shaped flowers that are usually pink or white with a red center. These flowers have a waxy texture and emit a sweet, honey-like fragrance, especially in the evening. Optimal conditions for blooming include bright, indirect light, proper watering, and slightly root-bound conditions.
 Pests and Diseases
Pests and Diseases
Pests
Common issues
Mealybugs
Spider mites
Scale insects
Aphids
Symptoms
Mealybugs: White, cottony masses on leaves and stems
Spider mites: Fine webbing, stippled leaves
Scale: Small, brown, shell-like bumps on stems
Aphids: Clusters of small, soft-bodied insects on new growth
Treatment
Isolate infected plants
Remove pests manually with a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol
Spray with neem oil or insecticidal soap
For severe infestations, use systemic insecticides
Improve air circulation and reduce humidity to prevent recurrence
Diseases
Common issues
Root rot
Leaf spot
Botrytis (gray mold)
Symptoms
Root rot: Wilting, yellowing leaves, mushy stems near soil
Leaf spot: Brown or black spots on leaves
Botrytis: Gray, fuzzy mold on leaves and flowers
Treatment
Root rot: Remove affected parts, repot in fresh, well-draining soil, reduce watering
Leaf spot: Remove affected leaves, improve air circulation, avoid overhead watering
Botrytis: Remove affected parts, reduce humidity, improve air circulation
Apply appropriate fungicide for persistent issues
Adjust care routine to prevent recurrence (e.g., proper watering, better drainage)
 Special Features
Special Features
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) is prized for its stunning variegated foliage, featuring creamy white or yellow patterns on green leaves. It produces clusters of star-shaped, waxy flowers that emit a sweet fragrance, especially in the evening. This plant is also known for its air-purifying qualities and its ability to thrive in hanging baskets or trained on trellises, making it a versatile and attractive addition to any indoor space.
 Plant Benefits
Plant Benefits
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) is primarily grown for ornamental purposes and does not have significant herbal or pharmaceutical benefits. However, it does offer air-purifying qualities, helping to remove indoor air pollutants. Some traditional medicine practices in its native regions have used Hoya species for various purposes, but these are not scientifically validated. The plant’s main benefits are aesthetic and its contribution to improving indoor air quality.
 Additional Information
Additional Information
The Variegated Wax Plant is a slow-growing, long-lived plant that can thrive for decades with proper care. It’s an excellent choice for collectors and enthusiasts due to its unique appearance and relatively low maintenance requirements. The plant’s vining nature makes it suitable for hanging baskets or training on trellises, adding versatility to its ornamental value.
 Life Cycle
Life Cycle
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) is a perennial epiphytic vine. In its natural habitat, it grows on trees or rocks, using them for support without parasitizing them. As a houseplant, it can live for many years with proper care. The plant grows slowly but steadily, producing new leaves and occasionally branching out. Mature plants (typically 2-3 years old) may produce flowers, which grow on specialized structures called spurs. These spurs should not be removed as they can rebloom multiple times. The plant doesn’t have a dormant period but growth slows in winter. With age, it can become quite large and may need support or training on a trellis or hoop.
 Are Variegated Wax Plant Poisonous, Toxic
Are Variegated Wax Plant Poisonous, Toxic
The Variegated Wax Plant (Hoya carnosa ‘Variegata’) is generally considered non-toxic to humans, cats, and dogs. However, ingestion of any plant material can potentially cause mild gastrointestinal upset in pets or children if consumed in large quantities.
Toxic parts: None specifically, but ingestion may cause mild irritation.
Affected organisms: While not toxic, it may affect cats, dogs, or children if ingested.
Symptoms of toxicity: Potential mild gastrointestinal upset, including vomiting or diarrhea.
Severity: Low
First aid steps: If ingestion occurs, rinse the mouth with water and drink water to dilute. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional or veterinarian.
Preventive measures: Keep the plant out of reach of pets and children who might be tempted to chew on the leaves. Educate family members about not ingesting houseplants.
 Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I water my Variegated Wax Plant?
Water your Variegated Wax Plant when the top 1-2 inches of soil feel dry. This is typically every 7-10 days during the growing season and less frequently in winter.
What kind of light does a Variegated Wax Plant need?
Variegated Wax Plants thrive in bright, indirect light. They can tolerate some direct morning sun but should be protected from harsh afternoon sunlight.
How do I propagate a Variegated Wax Plant?
Propagate Variegated Wax Plants through stem cuttings. Take a 4-6 inch cutting with 2-3 nodes, remove lower leaves, and plant in well-draining soil. Keep warm and humid until roots develop.
Is the Variegated Wax Plant toxic to pets?
The Variegated Wax Plant is generally considered non-toxic to pets. However, ingestion may cause mild gastrointestinal upset in some animals.
How often should I fertilize my Variegated Wax Plant?
Fertilize your Variegated Wax Plant every 2-4 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Why isn’t my Variegated Wax Plant flowering?
Variegated Wax Plants need to be mature (2-3 years old) to flower. Ensure it receives enough light, proper nutrition, and slightly root-bound conditions to encourage blooming.
How do I increase humidity for my Variegated Wax Plant?
Increase humidity by using a pebble tray filled with water, grouping plants together, using a room humidifier, or misting the leaves regularly.
When should I repot my Variegated Wax Plant?
Repot your Variegated Wax Plant every 2-3 years, or when it becomes root-bound. These plants prefer to be slightly root-bound, so don’t rush to repot.
How do I prune a Variegated Wax Plant?
Prune in spring or early summer by removing dead or yellowing leaves, trimming long vines to control size, and pinching off stem tips to encourage bushier growth. Avoid cutting off healthy spurs as these are future flowering sites.
What are common pests that affect Variegated Wax Plants?
Common pests include mealybugs, spider mites, scale insects, and aphids. Regularly inspect your plant and treat with neem oil or insecticidal soap if pests are detected.
 Can I grow Variegated Wax Plant in my indoor space
Can I grow Variegated Wax Plant in my indoor space
Difficulty
Size
Light
Water
Flowering
Pet Safe
Air Purifier
 Hoya carnosa 'Variegata' botanical details
Hoya carnosa 'Variegata' botanical details
Common Name
Other Common Names
Botanical Name
Native Area
Family Name
Plant Type
Genus
Kingdom
 Photo Gallery
Photo Gallery
- Perky Plant fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3RdLA00
- Seaweed extract: https://amzn.to/3z2CsFh
- Rooting hormone: https://amzn.to/3bIXi0t
- Espoma fertilizer: https://amzn.to/3vPa9bs
- Worm compost: https://amzn.to/3HVL01u
- Full-spectrum Light Bulb-Large: https://amzn.to/3yR6VBu
- Full-spectrum Lighting: https://amzn.to/3qhhaiv
- Light meter: https://amzn.to/4dpmp3s
- Moisture meter: https://amzn.to/3TEUu5N
- Hygrometer: https://amzn.to/3Cf6h2F
- Pruning shears: https://amzn.to/3X6oOcg
- ProMix Potting Soil: https://amzn.to/3iVIrjE
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: healthyhouseplants.storenvy.com
- My Perfect Pumice: Healthy Houseplants Store
- My Organic Green Gourmet Houseplant Fertilizer: Healthy Houseplants Store
As an Amazon Associate, I earn commission from qualifying purchases.
 Plant Puns and Jokes
Plant Puns and Jokes
Why did the Variegated Wax Plant refuse to climb the trellis? It was too ‘waxy’ to exercise!




 My Variegated Wax Plant Plant Care Recommendations
My Variegated Wax Plant Plant Care Recommendations Buy Variegated Wax Plant Online
Buy Variegated Wax Plant Online